Automobile Components:
An automobile component refers to any individual part or system that makes up a vehicle. These components work together to ensure that the vehicle operates properly, efficiently, and safely. Each component serves a specific function that contributes to the overall performance of the vehicle, from propulsion to safety and comfort.
Every time we get into a car, we rarely think about how the hundreds of components inside it work together to provide a smooth, safe, and efficient driving experience. From the engine to the wheels, each part plays a critical role in ensuring your vehicle operates effectively. In this article, we’ll take a closer look at the essential automobile components, explaining what they do and why they matter.
The Importance of Automobile Components:
Automobiles are complex machines composed of thousands of parts working together in harmony. These parts can be divided into several categories, including the engine system, transmission, electrical system, braking system, suspension, and more. Understanding how these components function and how they interact can help you appreciate the engineering behind modern vehicles and potentially save you from costly repairs.
Let’s break down some of the most important automobile components:
1. Engine
The engine is the heart of the vehicle. It converts fuel into mechanical energy, powering the car and enabling it to move. The engine operates on the principle of internal combustion, where fuel and air are mixed, compressed, and ignited to produce energy. There are different types of engines, such as gasoline, diesel, and electric engines, each with unique characteristics.
-
Gasoline Engine: Typically found in passenger vehicles, it uses spark plugs to ignite the fuel mixture.
-
Diesel Engine: Known for its fuel efficiency and power, it uses compression to ignite the fuel without the need for spark plugs.
-
Electric Engine: Electric engines run on electricity stored in batteries, offering a cleaner and quieter alternative to traditional internal combustion engines.
2. Transmission
The transmission system is responsible for transferring power from the engine to the wheels, allowing the vehicle to move at different speeds. It adjusts the power output from the engine depending on the driving conditions, ensuring the vehicle operates efficiently.
-
Manual Transmission: Involves the driver manually shifting gears using a clutch pedal and gear lever.
-
Automatic Transmission: Automatically shifts gears without input from the driver, making it more convenient for daily driving.
-
CVT (Continuously Variable Transmission): A type of automatic transmission that provides a seamless range of gears, improving fuel efficiency and driving comfort.
3. Braking System
The braking system is one of the most critical components for vehicle safety. It allows the driver to slow down or stop the vehicle when needed. Modern braking systems use hydraulic pressure to force brake pads against a rotor or drum, creating friction to reduce the vehicle’s speed.
-
Disc Brakes: These are the most common type, using brake pads to clamp onto a rotating disc (rotor).
-
Drum Brakes: Although less common today, drum brakes use shoes that press against the inside of a drum to slow the vehicle.
-
Anti-lock Braking System (ABS): ABS helps prevent the wheels from locking up during hard braking, improving control and safety.
4. Suspension System
The suspension system plays a vital role in maintaining vehicle stability and comfort. It connects the wheels to the vehicle’s frame and absorbs shocks from the road. This helps keep the car stable during driving, improves traction, and enhances passenger comfort by reducing vibrations.
Key components of the suspension system include:
-
Shock Absorbers: These dampen the impact from bumps and uneven surfaces, making the ride smoother.
-
Springs: Springs absorb energy from the road, helping to maintain balance.
-
Control Arms and Struts: These parts help keep the wheels in proper alignment and ensure smooth movement.
5. Electrical System
The electrical system is responsible for powering various components of the vehicle, such as lights, air conditioning, infotainment, and the ignition system. The primary power source is the car battery, which stores electrical energy and powers these systems when the engine is off.
The alternator recharges the battery when the engine is running, ensuring a steady supply of power. The starter motor is responsible for turning the engine over when starting the vehicle, while the fuse box protects electrical circuits from overload.
6. Fuel System
The fuel system is responsible for storing and delivering fuel to the engine. It ensures that the engine receives the correct amount of fuel in the right mixture for combustion.
Key components include:
-
Fuel Tank: Stores the fuel that powers the engine.
-
Fuel Pump: Delivers fuel from the tank to the engine.
-
Fuel Injectors: Spray fuel directly into the engine’s combustion chambers for efficient combustion.
7. Exhaust System
The exhaust system is responsible for directing harmful gases away from the engine and vehicle occupants. It channels the gases produced during combustion through various components, including the catalytic converter, which reduces harmful emissions before they exit the vehicle.
-
Muffler: Reduces noise produced by the exhaust gases.
-
Exhaust Pipes: Direct the gases out of the vehicle and ensure proper airflow.
8. Cooling System
The cooling system is designed to maintain the engine at an optimal temperature. It prevents the engine from overheating by circulating coolant (a mixture of water and antifreeze) through the engine block, absorbing heat, and releasing it through the radiator.
Key components of the cooling system include:
-
Radiator: Releases heat from the coolant to prevent the engine from overheating.
-
Thermostat: Regulates the flow of coolant, ensuring the engine stays within the proper temperature range.
-
Water Pump: Circulates the coolant through the engine and radiator.
9. Steering System
The steering system is responsible for controlling the direction of the vehicle. It allows the driver to turn the wheels and navigate the vehicle.
-
Rack-and-Pinion Steering: A common steering mechanism that converts rotational motion into linear motion to turn the wheels.
-
Power Steering: Uses hydraulic or electric assistance to make steering easier, especially at low speeds.
10. Wheels and Tires
The wheels and tires are crucial for providing traction and stability while driving. Tires are made from rubber and feature tread patterns that grip the road to ensure safe and efficient driving. The wheels, which hold the tires, are mounted to the axles and rotate to propel the vehicle forward.
-
Tires: Designed for specific driving conditions, such as all-season, winter, or performance tires.
-
Wheels: Made from steel, aluminum, or alloy, they support the tires and connect them to the vehicle.
11. Air Conditioning and Heating System
This system ensures that the cabin remains comfortable for the occupants, regardless of external weather conditions. The air conditioning system cools the air, while the heating system provides warmth during colder months.
-
Compressor: Pressurizes refrigerant to cool the air.
-
Evaporator: Absorbs heat and cools the air inside the cabin.
-
Heater Core: Uses hot coolant from the engine to warm the cabin.
Also explain with component image:
An automobile has several numbers of parts. But there are 4 essential automobile components are:
1. The Chassis.
2. The Engine.
3. The Transmission System.
4. The Body.
Engine:
The engine is consists of an I.C. Engine (Internal Combustion Engine) which converts chemical energy of fuel into thermal energy and then thermal energy to mechanical energy in the form of rotary motion crank shaft. This motion is given to flywheel. At flywheel, by using dynamometer (Eddy current dynamotor, hydraulic dynamometer, etc.), we get brake power by measurement of torque.
The various types of engines are:
(i) in-line Engine,
(ii) V- type Engine,
(iii) W-type Engine,
(iv) Opposed Cylinder Engine,
(v) Radial Engine,
(vi) Reverse Engine,
(Vii) Single Engine,
(viii) Horizontal Engine.

Frame:
Frame is the metallic part of chassis which is manufactured from channels ad angles joined by arc welding. On the frame, various parts of vehicles are mounted.
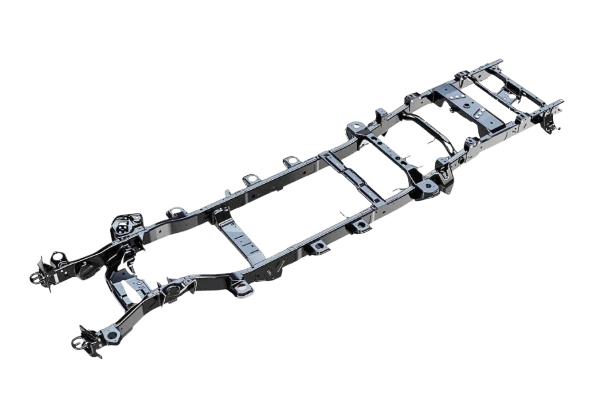
Clutch:
Clutch is connected after engine and before gearbox and it transfers the drive from engine to gearbox. Clutch is important part of vehicle.
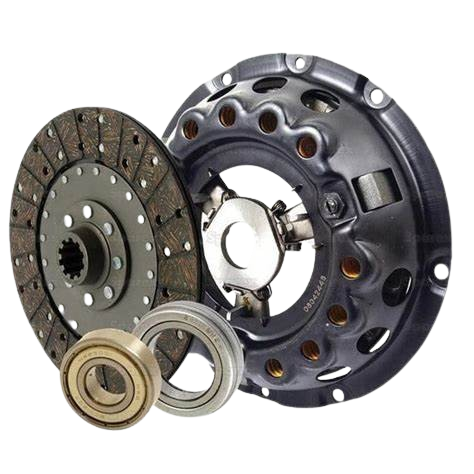

Functions of clutch are as follows:
(i) To allow engagement and disengagement of engine with transmission system, at the will of the driver, when automobile is stationery and engine is running (idling).
(ii) To absorb minor shocks and vibrations while transmitting engine power to the wheels when the vehicle starts from stationary position.
(iii) To allow changing gears from first to second or second to third, etc. as per the drivers need.
(iv) To ensure smooth engagement of gears without damaging gear teeth. Clutch and drive can be easily engaged and disengaged by a pedal provided at the foot region in the driver’s cabin (for four-wheeler) or manually by hand (for two wheelers).
Gear Box:
Gear box fitted in between clutch and propeller shaft assembly. It provides the necessary variation of torque and speed available from engine to the propeller shaft. In order to enable the engine to run faster in relation to the road wheel as well as to multiply the torques, a gear box is used.

Propeller shaft:
It is also a drive element which is fitted in between Gear box output shaft and the differential on the rear axle.
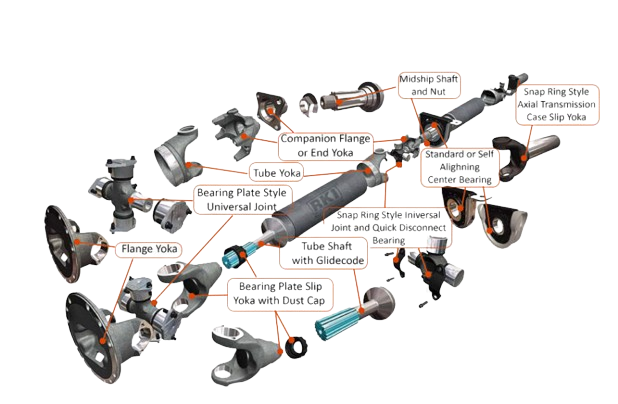
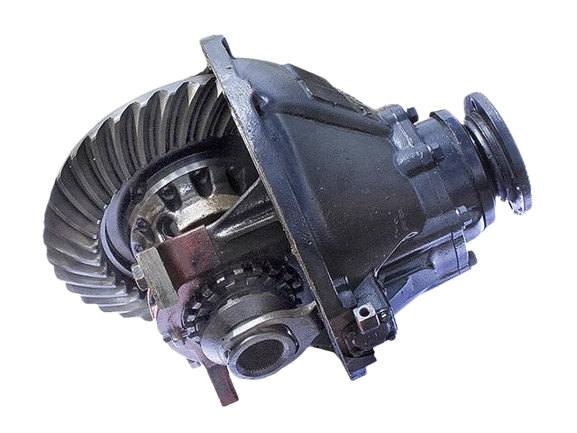
Differential:
It is used to achieve different speeds on inner and outer driving w eels when the vehicle is taking turn or when the vehicle is negotiating a curve.

Rear axle:
It consists of driving shaft inside a hollow tubular structure. Wheels are driven; rear axle is same as the drive axle.

Front axle:
This mainly consists of steering mechanism, stub axle and wheels mounted at the extreme ends.
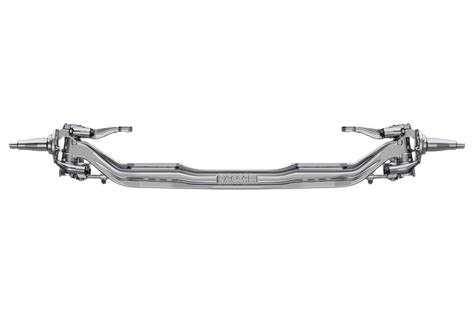
Wheels:
These are the last elements in the drive chain. The main purpose of the wheels is to support the entire load on the vehicle.

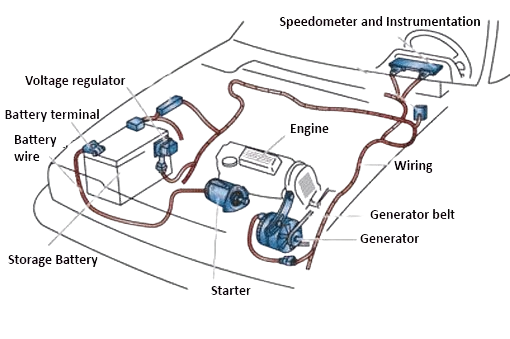
Electrical accessories:
This usually includes starter motor, battery, alternator, brake lights etc.
Recent Comments